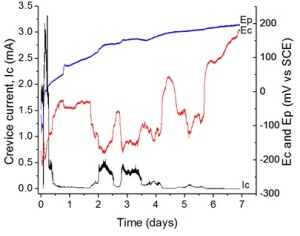
Electrochemical measurements of the crevice current, Ic, and the crevice potential, Ec, (Figure 1) show the progression of the crevice corrosion. The planar potential, Ep, is from the planar electrode, which does not have a crevice, and is used as a comparison to Ec. The crevice current is a measure of the consumption of dissolved oxygen, the supporting cathodic reaction driving crevice corrosion. The relationship between Ic and Ec is clear. The variation of Ic with time suggests a number of periodic, short crevice corrosion events.
By Thalia Wells, Department of Chemistry, Western University

